MTaPS' Support
In its Asia bureau, MTaPS set out to advance pharmaceutical management systems in the Asia region. The initiative aimed to strengthen the region’s capacity to institutionalize transparent and evidence-based decision-making, to generate and use robust information to define and cost pharmaceutical coverage, and to improve the regulation and governance of the of the pharmaceutical sector.
MTaPS focuses on the following technical areas:
Improving the efficiency of pharmaceutical resource allocation
Health technology assessment
MTaPS is playing a pivotal role in advancing health technology assessment (HTA) in Asia. This includes the collaborative development, in partnership with global thought leaders, of an extensive HTA roadmap based on a systematic review , fostering the institutionalization of HTA practices in the region. MTaPS has conducted in-depth assessments of nine countries/territories in Asia, introducing the innovative HTA institutionalization canvas to comprehensively evaluate HTA systems. MTaPS has provided hands-on support to countries based on the needs identified at the HTAsiaLink conference, resulting in HTA institutionalization in Indonesia and guidance for medical device assessment in the Philippines. The evaluation of the need for an HTA hub has led to a recommendation to strengthen HTAsiaLink's existing initiatives, aligned with a commitment to HTA best practices in Asia.
Pharmaceutical expenditure tracking
MTaPS reviewed tools to cost pharmaceutical benefits packages and developed training resources for regional OneHealth Tool (OHT) capacity-strengthening initiatives. MTaPS has made significant progress in implementing the OHT and conducting regional capacity-strengthening sessions on pharmaceutical expenditure (PE) tracking in Asian countries. That includes the completion of Bangladesh Social Health Protection (SHP) benefits costing and the development of dissemination resources for PE tracking standardization in the Asian region. In Indonesia, MTaPS also provided technical assistance to customize the Health Accounts methodology to produce higher quality and detailed data on pharmaceutical spending. Indonesian PE tracking was implemented in close collaboration with the Center for Health Financing and Decentralization Policy (Pusjak PDK) team and the Health Accounts team.
Regulatory systems strengthening
MTaPS has collaboratively worked with regional and sub-regional entities in Asia, including the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Southeast Asian Regulatory Network (SEARN), and country national regulatory authorities (NRAs), to strengthen their pharmaceutical regulatory systems to ensure the availability of, and access to, safe, high quality, and efficacious medical products. Aligning the support to World Health Organization (WHO) Global Benchmarking Tool to enhance the maturity levels of NRAs, MTaPS has:
- Helped countries adopt model pharmaceutical legislation, policies, guidelines, and norms.
- Established mechanisms for oversight and enforcement of policies, laws, and regulations.
- Developed NRAs' regulatory capacity through on-the-job training, knowledge sharing, and adaptation of model tools.
- Supported convergence of medicine registration and harmonization efforts through regional networks like ASEAN and SEARN.
Strengthening pharmaceutical sector governance
Strengthening pharmaceutical sector governance
MTaPS partnered with the Philippines Department of Health (DOH) to enhance strategic procurement mechanisms, focusing on pooled procurement (PPM). A comprehensive legal analysis was conducted to assess the frameworks affecting PPM implementation, resulting in recommendations. The DOH then developed and submitted a PPM policy proposal to the Government Procurement Policy Board. To support the policy's piloting, MTaPS analyzed medicine sales data, identifying priority medicines, local government units (LGUs), and hospitals for PPM engagement. A draft implementation plan was created, involving desk reviews, data collection, and interviews. Additionally, MTaPS studied bid failures in DOH’s procurement of HIV, TB, and FP products, identifying root causes and providing 17 recommendations. The findings were summarized in a "Technical Advisory" for the DOH to improve procurement outcomes and reduce resource wastage.
Conflicts of Interest (COI)
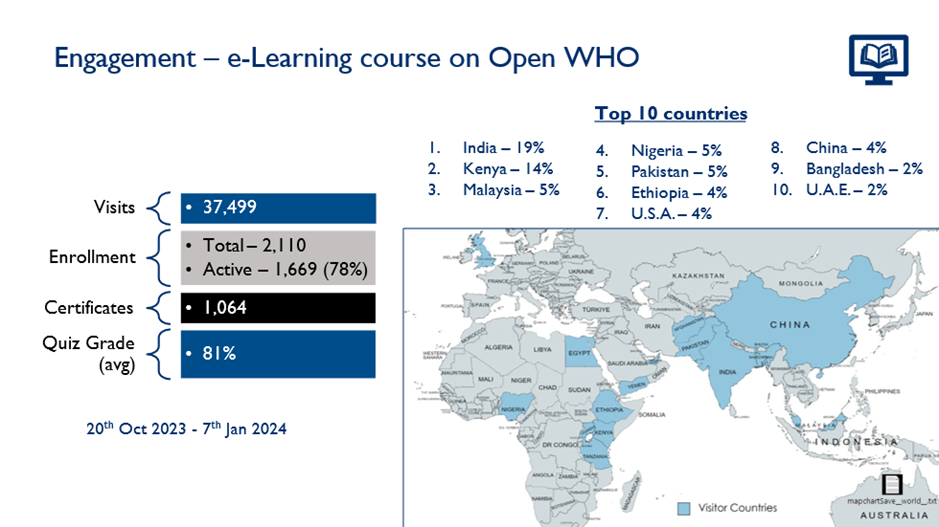
Avoiding COI between decision makers and the private sector is a major step toward creating strong sectoral governance structures. MTaPS assessed the region’s COI landscape and collaborated with the WHO to develop a manual for preventing and managing COI. The manual highlights 10 critical steps for improving COI policy, prevention, and management in public pharmaceutical decision-making committees. These steps build upon four overarching principles of managing COI: proportionality, transparency, accountability, and fairness. Through a Joint Learning Exchange activity, officials from 12 countries shared their experiences with COI and the application of the manual. Subsequently, an eLearning course was developed on preventing and managing COI. As of March 30, 2024, more than 1,400 people had completed the course.